SDAA101 September 2025 TDP142-Q1 , TDP2044 , TUSB1021-Q1 , TUSB1044 , TUSB1044A , TUSB1064-Q1 , TUSB1142 , TUSB1146 , TUSB521-Q1 , TUSB542 , TUSB544 , TUSB5461-Q1 , TUSB564 , TUSB564-Q1
1.1 What is USB?
Universal Serial Bus, or USB is a serial protocol that allows for communication from a USB host to a USB device. This protocol was originally introduced in 1996, and today is one of the most popular communication protocols in the world. USB is used in applications ranging from mobile phones to electrical vehicles. Since 1996 there have been many updates and improvements to the protocol specification that led to popularity. As shown in Table 1-1, the major revisions of the USB in use today are USB 2.0, USB 3.2, and USB 4.
| USB Version | Symbol | Data Rate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| USB 2.0 | LS | Low-Speed |  |
1.5Mbps |
| FS | Full-Speed | 12Mbps | ||
| HS | High-Speed |  |
480Mbps | |
| USB 3.2 | Gen 1 | SuperSpeed |  |
5Gbps |
| Gen 2 | SuperSpeed 10Gbps |  |
10Gbps | |
| Gen 2x2 | SuperSpeed 20Gbps |  |
20Gbps | |
| USB 4 |  |
40Gbps |
The latest revision of the USB is always backwards compatible with the previous iteration. This means a USB port supporting the newest revision, USB 4 with communication speeds of 40Gbps, is also required to support the oldest revision, USB 2.0 Low Speed with a communication speed of 1.5Mbps.
When USB transitioned from USB2 to USB3.x there was a major change in the physical characteristics of the USB port.
- In USB2.0 speeds all communication take place between a single DC-coupled differential pair utilizing half-duplex communication. (bidirectional communication across a single channel)
- In USB3.2 onwards the communication takes place across two AC-coupled differential pairs allowing for full duplex communication. (unidirectional communication across two channels)
The USB specification also defines standard connectors associated with the USB protocol. The following diagram highlights the different USB connectors and the footprints:
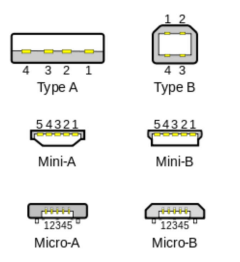 Figure 1-1 Typical USB 2.0 Connector
Types
Figure 1-1 Typical USB 2.0 Connector
TypesHere a link to the USB website for more details: USB Document Library